
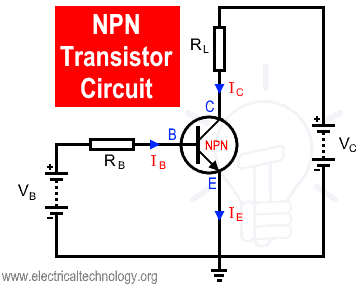
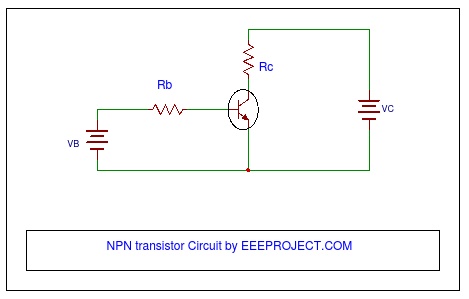
14īeta () represents the amplification factor of a transistor.

When IB = 0 A the transistor is in cutoff, but there is some minority current flowing called ICEO. This is usually so small that it can be ignored, except in high power transistors and in high temperature environments.where ICBO = minority collector current.12Ĭollector Characteristics Base Characteristics Common-Emitter Characteristics 13 The input is on the base and the output is on the collector. Voltage Gain: Transistor Amplification Currents and Voltages: 11Ĭommon–Emitter Configuration The emitter is common to both input (base-emitter) and output (collector-emitter). In reality: a is between 0.9 and 0.998 10.8Īpproximations Emitter and collector currents: Base-emitter voltage: 9Īlpha () relates the DC currents IC and IE : Alpha () in the AC mode: Alpha (a) Cutoff-The amplifier is basically off.Active-Operating range of the amplifier.6Ĭommon-Base Amplifier Output Characteristics This graph demonstrates the output current (IC) to an output voltage (VCB) for various levels of input current (IE). 5Ĭommon-Base Amplifier Input Characteristics This curve shows the relationship between of input current (IE) to input voltage (VBE) for various levels of output voltage (VCB). The base-collector junction is reverse biased 3Ĭurrents in a Transistor Emitter current is the sum of the collector and base currents: The collector current is comprised of two currents: 4Ĭommon-Base Configuration The base is common to both input (emitter–base) and output (collector–base) of the transistor.The emitter-base junction is forward biased.Transistor Operation With the external sources, VEE and VCC, connected as shown below:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
