
We further focus on the recent findings of their catabolic mechanism by lipolysis and autophagy as well as their connection ragarding the regulation and function. In this review, we first provide an overview of the current knowledge on the structural properties and the biogenesis of LDs. Lipolysis and autophagy are two main catabolic pathways of LDs, which regulate lipid metabolism and, thereby, closely engaged in many pathological conditons. Degradation of LDs provide metabolic energy for divergent cellular processes such as membrane synthesis and molecular signaling. They are composed of a hydrophobic neutral lipid core surrounding by a phospholipid monolayer membrane with various decorating proteins. LDs are evolutionary conserved organelles found in almost all organisms, from bacteria to mammals. In this entry, we will summarize our knowledge on structural diversity of lipids providing information on the various lipid classes and also fatty acids and lipid mediators that occur naturally.Lipids are essential building blocks synthesized by complex molecular pathways and deposited as lipid droplets (LDs) in cells. In addition to a structural role, lipids serve as important intermediates in cell signaling pathways (e.g., sphingolipids, inositol lipids, phosphatidic acid, lysophospholipids, oxidative products) and play a role in mediating cellular responses to the environment (Gunstone et al. Waxes as surface coverings are integral to water balance and also protect organisms from noxious environmental conditions. Arranged as bilayers, they establish permeability barriers for cells and organelles and provide a microenvironment for membrane-associated proteins as well as directly participating in metabolism and a multitude of membrane fusion events (Gurr et al. Polar lipids and sterols are important structural components of cell membranes where they may have many diverse functions. Triacylglycerols act as energy stores and metabolic fuels. According to their structures, lipids can be divided into two main groups: the nonpolar lipids (acylglycerols, sterols, nonesterified (free) fatty acids, hydrocarbons, alcohols, wax, and steryl esters) and polar lipids (phosphoglycerides, glycosyl glycerides, and sphingolipids).
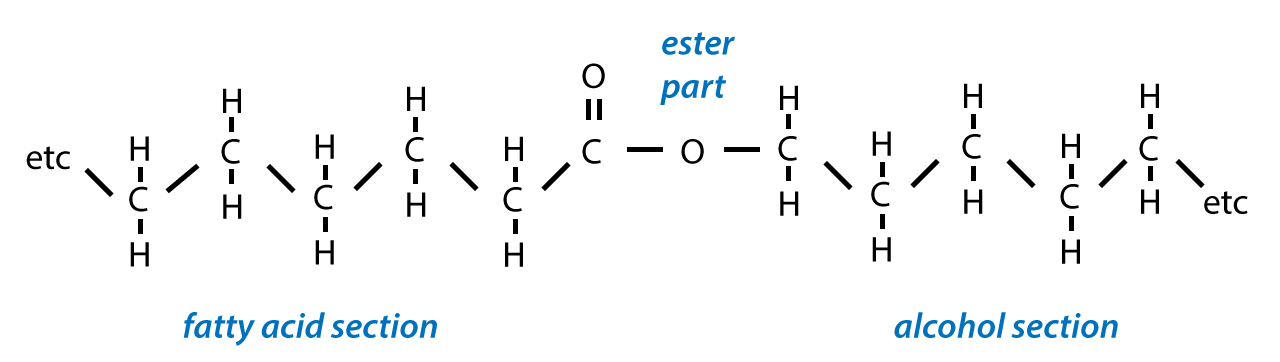
The wide range of chemical and physical properties of different lipids determines a variety of roles for these compounds in biological processes.
Lipids represent some of the most complex biological molecules, and their diversity is crucial for their cellular functions. Restricted to Repository staff only until 9 December 2023 due to copyright restrictions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
